Introduction to Amantadine and Traumatic Brain Injury
As someone who has been affected by a traumatic brain injury (TBI), I know that finding the right treatment can be a difficult journey. After much research, I came across Amantadine, a medication that has shown promising results in managing the symptoms of TBI. In this article, I will discuss the various aspects of Amantadine and how it can potentially help those suffering from traumatic brain injuries.
Amantadine is a medication originally developed to treat influenza, but it has since been found to have various other uses, including treating Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis. Recently, it has been studied for its potential benefits in treating the cognitive and behavioral symptoms associated with TBI. Let's dive into the different sections of this article to learn more about Amantadine and its possible role in TBI management.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
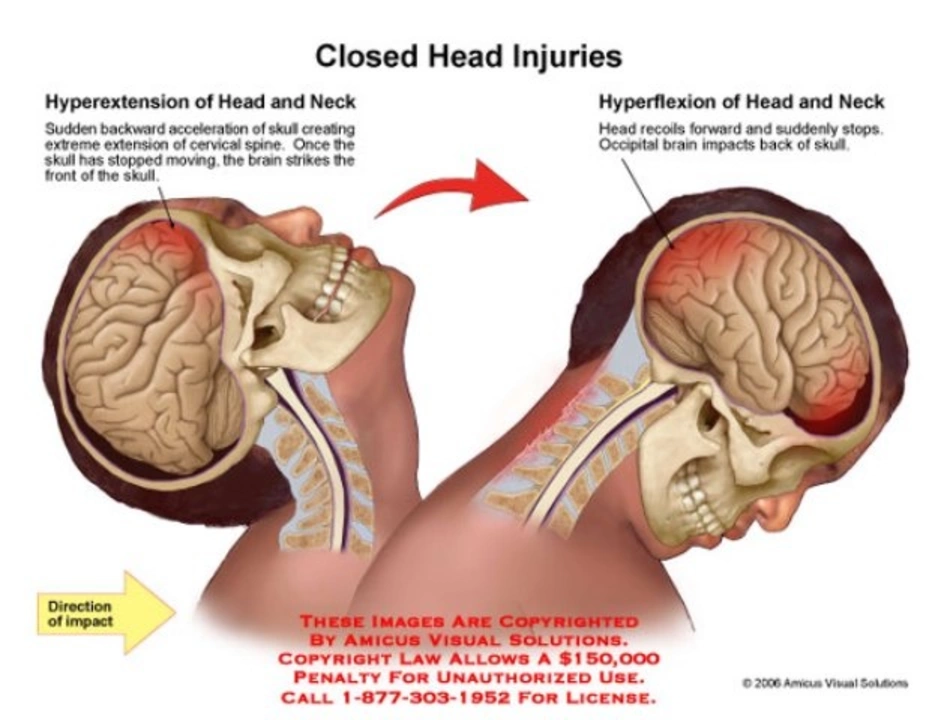
Before we delve into the benefits of Amantadine, it is essential to understand what a traumatic brain injury is and its potential impact on a person's life. A TBI occurs when an external force, such as a blow to the head or a penetrating injury, disrupts the normal function of the brain. This can result in various symptoms, including cognitive, physical, emotional, and behavioral changes.
Every TBI is different, and the severity of the injury can range from mild to severe. Some common symptoms of TBI include memory problems, headaches, dizziness, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can significantly affect a person's ability to perform daily tasks and maintain relationships, making it crucial to find effective treatment options.
Amantadine's Mechanism of Action
Amantadine works by increasing the release of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter crucial for various brain functions, including mood regulation, reward, and movement. In the context of TBI, the increase in dopamine levels can help improve cognitive and motor function, as well as alleviate some of the emotional and behavioral symptoms associated with the injury.
While the exact mechanism of action for Amantadine in TBI is still being researched, it is believed that the medication may also have neuroprotective properties. This means that Amantadine could potentially help protect the brain from further damage after a traumatic injury, promoting the healing process and improving overall outcomes.
Research Supporting Amantadine's Effectiveness in TBI
Several studies have explored the potential benefits of Amantadine for TBI patients. One such study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that patients with TBI who received Amantadine showed significant improvements in cognitive function, motor skills, and overall recovery compared to those who received a placebo.
Another study published in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation found that Amantadine could help improve attention and memory in TBI patients, as well as reduce irritability and aggression. These findings suggest that Amantadine may be a promising treatment option for managing TBI symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
Amantadine's Potential Side Effects
As with any medication, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects of Amantadine. Some common side effects include dizziness, lightheadedness, insomnia, and gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and diarrhea. More severe side effects may include hallucinations, seizures, and an irregular heartbeat.
It is crucial to discuss these potential side effects with your healthcare provider before starting Amantadine treatment. They will be able to determine if Amantadine is a suitable option for you and monitor your progress to ensure your safety throughout treatment.
Dosage and Administration of Amantadine
The dosage of Amantadine for TBI patients can vary depending on individual factors, such as the severity of the injury and the patient's overall health. It is typically taken orally, either as a tablet or a liquid solution. The medication is usually started at a low dose, which is gradually increased over time to minimize the risk of side effects and allow the body to adjust to the medication.
It is vital to follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding dosage and administration, as they will determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs. Do not stop taking Amantadine suddenly, as this may cause withdrawal symptoms. Instead, discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider, who can advise you on how to safely taper off the medication if necessary.
Amantadine as Part of a Comprehensive TBI Treatment Plan
While Amantadine has shown promise in managing the symptoms of TBI, it is essential to remember that it should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. This may include other medications, cognitive rehabilitation therapy, physical therapy, and support from a team of healthcare professionals.
By combining Amantadine with other treatments and therapies, you may increase the likelihood of a successful recovery and improve your overall quality of life. It is crucial to communicate with your healthcare team and stay proactive in your treatment journey to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion: Amantadine's Potential Role in TBI Management
In conclusion, Amantadine is a medication with potential benefits for those suffering from traumatic brain injuries. Its ability to increase dopamine levels in the brain may help improve cognitive function, motor skills, and emotional well-being, making it a promising treatment option for managing TBI symptoms.
As with any medication, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects and work closely with your healthcare provider to determine if Amantadine is right for you. By incorporating Amantadine into a comprehensive treatment plan and staying proactive in your recovery journey, you may improve your overall quality of life and increase your chances of a successful recovery.

Lucinda Harrowell
May 7, 2023 AT 01:01Joe Rahme
May 8, 2023 AT 20:35Leia not 'your worship'
May 10, 2023 AT 20:14Jo Sta
May 11, 2023 AT 08:05KALPESH GANVIR
May 12, 2023 AT 00:29April Barrow
May 12, 2023 AT 17:24Melody Jiang
May 13, 2023 AT 17:30alex terzarede
May 13, 2023 AT 18:02Dipali patel
May 15, 2023 AT 04:13Jasmine L
May 16, 2023 AT 13:05lisa zebastian
May 16, 2023 AT 15:28Jessie Bellen
May 17, 2023 AT 17:58Jasmine Kara
May 19, 2023 AT 16:13Richie Lasit
May 20, 2023 AT 19:10arthur ball
May 21, 2023 AT 13:14