Chelation Therapy: What It Is, How It Works, and What the Evidence Says
When you hear chelation therapy, a medical treatment that binds heavy metals in the bloodstream so they can be removed through urine. Also known as metal chelation, it’s a proven tool for treating acute heavy metal toxicity—like lead or mercury poisoning. But it’s also been marketed as a cure-all for heart disease, autism, and aging. The truth? Only a few uses have solid science behind them.
The most common form uses EDTA, a synthetic amino acid that grabs onto metals like iron, lead, or cadmium and carries them out of the body. Doctors use it in hospitals when someone has dangerously high levels of these toxins—often from old paint, contaminated water, or industrial exposure. For these cases, chelation isn’t just helpful—it’s life-saving. But outside of that, the evidence gets murky. Some clinics push it for heart disease, claiming it clears plaque from arteries. Yet large studies, including one by the NIH, found only a small benefit for a specific group of heart patients with diabetes and prior heart attacks. No major health group recommends it as a standard treatment for heart disease.
There are risks too. Chelation can strip away essential minerals like zinc and calcium if not monitored. Kidney damage, low blood sugar, and irregular heart rhythms have happened when it’s given too fast or to the wrong person. And while some people swear by it for detox or energy boosts, there’s no proof it works for those claims. If you’re thinking about it, ask: Are you being treated for a confirmed metal overload? Or are you being sold a solution without a diagnosis?
Below, you’ll find real patient-focused guides that cut through the noise. Learn how to read drug warnings that might apply to chelation agents, what to ask your doctor before starting, and how to spot unsafe practices. You’ll also see how other treatments—like managing kidney disease or avoiding dangerous drug interactions—tie into the bigger picture of safe, science-backed care. This isn’t about hype. It’s about knowing what actually works, and what doesn’t.
 1 Dec 2025
1 Dec 2025
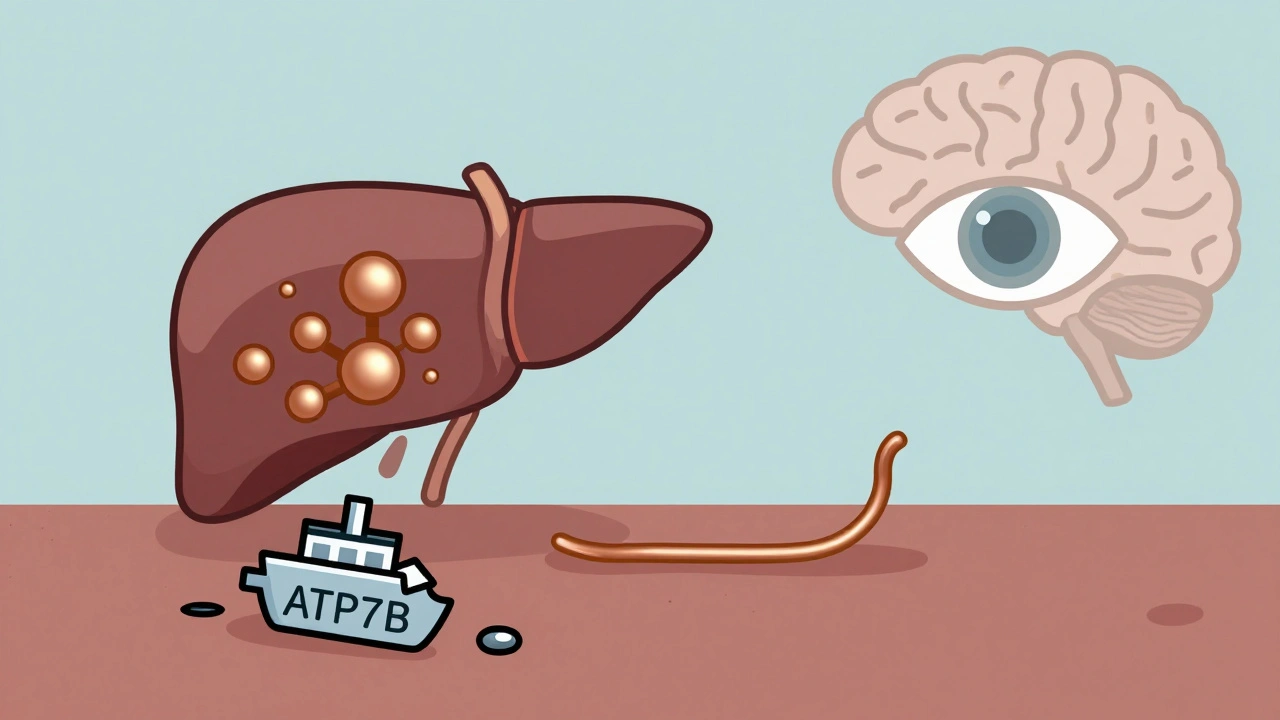
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder causing toxic copper buildup in the liver and brain. Early diagnosis and chelation therapy can prevent organ damage and allow a normal lifespan. Learn how copper accumulates and how treatments like penicillamine, trientine, and zinc work.
View More

