Hypertriglyceridemia: Causes, Risks, and Medications That Help
When your blood has too many triglycerides, a type of fat that stores excess energy from your diet. Also known as high blood fat, it’s not just a lab result—it’s a silent signal that something’s off in how your body handles sugar, fat, or insulin. If you’ve been told your triglycerides are over 150 mg/dL, you’re not alone. Millions of people with diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome deal with this daily. And left unchecked, it doesn’t just sit there—it raises your risk of heart attacks, strokes, and even a painful condition called acute pancreatitis.
This isn’t just about diet or exercise, though those matter. Many people with hypertriglyceridemia, a medical condition defined by persistently elevated triglyceride levels. Also known as familial hypertriglyceridemia when inherited, it often needs more than lifestyle changes to manage. That’s where medications come in. Drugs like fibrates, a class of medications that lower triglycerides by reducing liver fat production and boosting fat breakdown are common. So are statins, though they’re better known for cholesterol. Niacin and omega-3 fatty acids in prescription doses also show up in treatment plans. But here’s the catch: these meds don’t work the same for everyone. Someone with diabetes might need a different approach than someone with heavy alcohol use or genetic causes. And some drugs, like certain steroids or beta-blockers, can actually make it worse.
What you’ll find in the posts below isn’t a generic list of pills. It’s real-world insight into how these drugs interact with other conditions you might have—like diabetes, kidney issues, or heart disease. You’ll see how hypertriglyceridemia ties into polypharmacy risks, how it affects people on blood thinners, and why some meds that help one thing can hurt another. There’s no fluff. Just clear, practical info on what works, what doesn’t, and what to watch out for when your numbers are high and your meds are piling up.
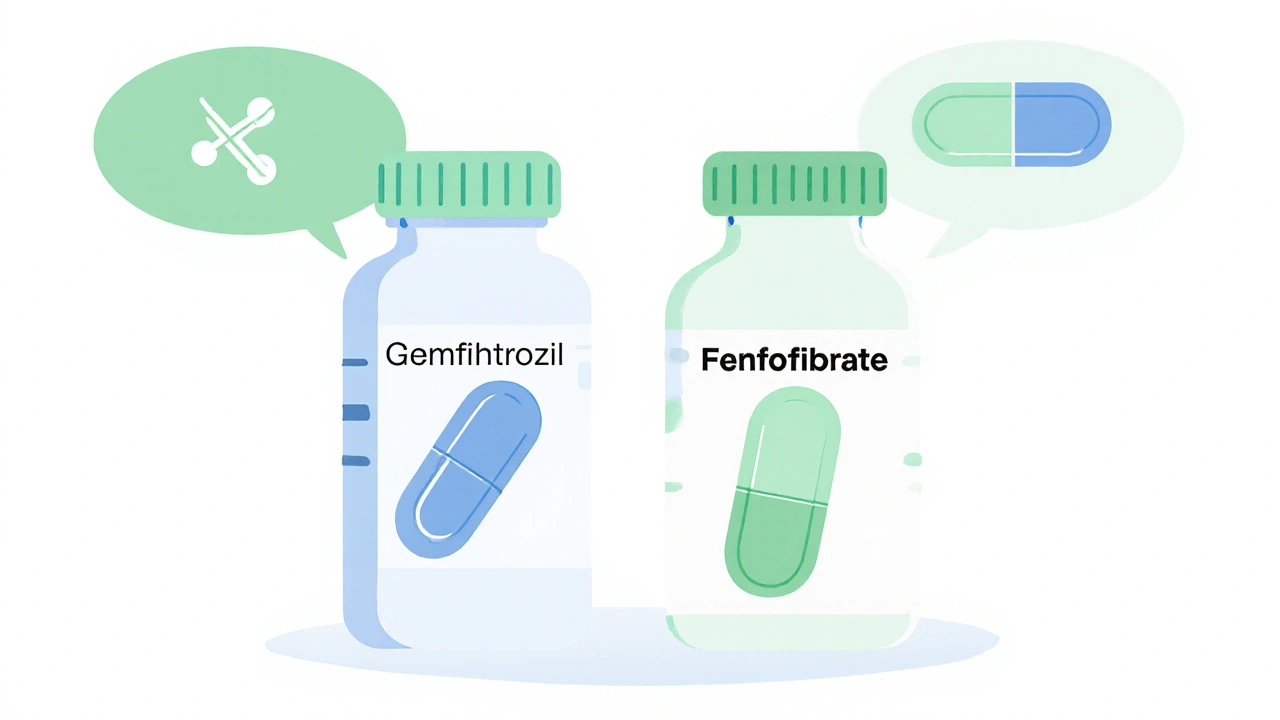 22 Oct 2025
22 Oct 2025
A clear guide comparing gemfibrozil and fenofibrate, covering mechanisms, uses, dosing, side effects, interactions, costs and FAQs for patients and clinicians.
View More

